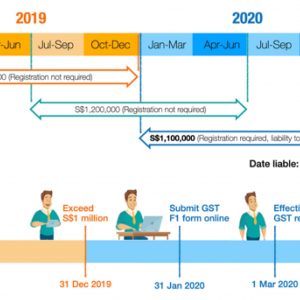
Business Organisations in Singapore
In Singapore, companies are principally governed by the Companies Act (Cap 50, 2006 Rev Ed) (hereinafter “the Act”). It should be noted though that specific types of companies may, in addition to the Companies Act, be regulated by other statutes.
Business organisations can either be incorporated or unincorporated. Incorporation involved creating a separate legal entity. The separate legal entity created can incur its liabilities and have its own rights that are distinct from those of the owners or creators of the entity. The most common forms of incorporated organisations are the company and the limited liability partnership, though there are others such as statutory boards and management corporations. The most common forms of unincorporated organisations are the sole partnership, the partnership and the limited partnership, though there are others such as business trusts.
Read: Comparison of Business Entities in Singapore
Setting up a wrong type of organisation to run a business may affect the business and may affect the owner of the business, although it may be possible to dissolve one form of structure and set up another. Generally speaking, the cost of setting up the wrong type of organisation may be higher than running the business.
Know the Types of Business Organisations First
Importantly before you start your business in Singapore, get to know about the types of business entity you could choose from.
There are 4 main types of business structures to choose from. They are:
- Sole-Proprietorship (one owner) or Partnership (two or more owners)
- Limited Partnership (LP)
- Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
- Company
1.Sole-Proprietorship (one owner) or Partnership (two or more owners)
Definition: A business owned by 1 or more person
Registration requirements: Singapore Citizen/Singapore Permanent Resident/EntrePass
Legal status:
- Not a separate legal entity
- Owner/Partners has unlimited liability
- Cannot own property in the firm’s name
- The owner is personally liable for debts and losses of the business, Partners personally liable for partnership’s debts and losses incurred by other partners
Tax: Profits taxed at owner’/partners’ personal income tax rates
2. Limited Partnership (LP)
Definition: A partnership consisting of two or more persons, with at least one general partner and one limited partner
Registration requirements: If all general partners are ordinarily resident outside Singapore, they must appoint a local manager who is ordinarily resident in Singapore.
Legal status:
- Not a separate legal entity
- The general partner has unlimited liability
- The limited partner has limited liability
- Cannot own property in the firm’s name
- General partner personally liable for debts and losses of the LP
Tax: Profits taxed at partners’ personal income tax rates (if individual)/ corporate tax rate (if corporation)
3. Limited Liability Partnership (LLP)
Definition: A partnership where the individual partner’s liability is generally limited
Registration requirements: At least one manager ordinarily resident in Singapore
Legal status:
- A separate legal entity from its partners
- Partners have limited liability
- Can own property in LLP’s name
- Partners personally liable for debts and losses resulting from their wrongful actions
- Partners not personally liable for debts and losses of LLP incurred by other partners
Tax: Profits taxed at partners’ personal income tax rates (if individual)/ corporate tax rate (if corporation)
4.Company
Definition: A business form which is a legal entity separate and distinct from its shareholders and directors.
Registration requirements: At least one shareholder (could be a foreigner). At least one director is ordinarily resident in Singapore.
Legal status:
- A separate legal entity from its members and directors
- Members have limited liability
- Can own property in the company’s name
- Members not personally liable for debts and losses of the company
Tax: Profits taxed at corporate tax rates
Foreign Companies Considering Expanding Your Business to Singapore
If you are a foreign company planning to expand your business in Singapore. Here are options for Singapore company incorporation you may wish to know before proceeding further.
Before you decide on your business type, please note:
- A Singapore Representative Office would not be applicable if you do any income-generating activities.
- A Singapore Branch Office must have the same business activities and name as the parent company.
|
Singapore Branch office |
Singapore Subsidiary Company |
SINGAPORE REPRESENTATIVE OFFICE |
|
|
Legal Type: |
Not a separate legal entity but an extension of the parent company |
Separate legal entity distinct from its parent company |
Has no legal status, a temporary administrative arrangement |
|
Liabilities: |
Liabilities extend to the parent company |
Liabilities limited to subsidiary |
Liabilities extend to the parent company |
|
Entity Name: |
Must be the same as the parent company |
Can be the same or different from parent company |
Must be the same as parent company plus must include ‘Representative Office’ |
|
Allowed Activities: |
Must be the same as the parent company |
Can be the same or different from parent company |
Can only conduct market research or feasibility studies |
|
Validity Period: |
Registered forever until closed |
Registered forever until closed |
Must be renewed every year up to a maximum of 3 years |
|
Normal Registration Time: |
1-2 days |
1-2 days |
3-5 days |
|
Taxation: |
Taxed as a non-resident entity, local tax benefits not available |
Taxed as Singapore resident entity, local tax benefits available |
Not applicable as the representative office cannot generate income |
|
Annual Filing: |
Must file branch office as well as parent company’s accounts |
Must file accounts of the Singapore subsidiary |
Not applicable |
|
Bank Account: |
Can open a bank account in Singapore |
Can open a bank account in Singapore |
Can open a bank account in Singapore but must be funded by the parent company. |
|
Staff Hiring: |
No restrictions on hiring local or foreign staff |
No restrictions on hiring local or foreign staff |
Chief Representative must be a staff member from the parent company. Can have only five employees. |
Read: Choosing a Business Structure
While some businesses choose to act on their own, others turn to Acrabiz or service providers for assistance. Designating us as your appointed agent has many advantages. Our clients have benefited from our physical availability to act for them all the time. Our works are organised and as the gatekeeper between your business and the authority, you can be assured the authorities will receive high-priority, quality paperwork every time. Nothing is accidentally lost or forgotten.
Need support to incorporate the right type of business? Let Acrabiz help you as your business advisor and corporate secretary!
Contact Us